Quick Start
Tutorial Video
Watch our tutorial to get started with HumaLab SDK:
Get up and running with HumaLab SDK in just a few minutes.
Installation
Install HumaLab SDK using pip:
pip install humalabAuthentication
Before using HumaLab, configure your authentication:
Configure with login()
import humalab as hl
# Configure once
hl.login(api_key="your_api_key", host="https://api.humalab.ai")
# Then use init without credentials
with hl.init(project="my_project", scenario={...}) as run:
passYou can get your API key from the HumaLab platform dashboard.
Your First Run
Here's a complete example to run your first validation experiment:
import humalab as hl
from humalab.humalab_api_client import EpisodeStatus
# Initialize and create a run with context manager
with hl.init(
project="physics_sim",
name="wind_gravity_test",
description="Testing different physics parameters",
tags=["physics", "simulation"],
scenario={
"gravity": "${uniform: -10, -9}",
"friction": "${gaussian: 0.5, 0.1}",
"wind_speed": "${uniform: 0, 5}"
},
) as run:
# Execute episodes
for i in range(10):
with run.create_episode() as episode:
# Access sampled parameters directly
print(f"Episode {i}:")
print(f" Gravity: {episode.gravity}")
print(f" Friction: {episode.friction}")
print(f" Wind: {episode.wind_speed}")
# Run your validation logic here
# result = run_simulation(
# gravity=episode.gravity,
# friction=episode.friction,
# wind_speed=episode.wind_speed
# )
# Log the results
episode.log({
"success": result.success,
"final_distance": result.distance,
"simulation_time": result.time
})
print("Experiment complete! Check the HumaLab platform to view results.")Key Concepts Explained
1. Scenarios
Scenarios define the parameter space using probability distributions:
scenario = {
"parameter1": "${uniform: 0, 10}", # Uniform from 0 to 10
"parameter2": "${gaussian: 5, 0.01}", # Gaussian with mean=5, std=0.01
"parameter3": "${bernoulli: 0.7}" # 70% chance of 1, 30% of 0
}2. Runs
Runs organize your experiments:
run = hl.Run(
scenario=scenario,
project="my_project", # Organize by project
name="experiment_1", # Name this specific run
tags=["baseline", "test"] # Add searchable tags
)3. Episodes
Each episode is one execution with specific sampled parameters:
with run.create_episode() as episode:
# Access sampled parameters directly
value = episode.my_param
# Or via scenario property
config = episode.scenario
# Log results
episode.log(results)Adding Metrics
Track metrics across episodes:
# Create a metric
from humalab.constants import GraphType
metric = hl.metrics.Metrics(
graph_type=GraphType.LINE
)
# Add to run
run.add_metric("success_rate", metric)
# Log across episodes
successes = 0
with run:
for i in range(100):
with run.create_episode() as episode:
result = validate(episode)
if result.success:
successes += 1
# Log cumulative success rate
run.log({"success_rate": successes / (i + 1)})Navigating the GUI
At the first glance, you will see the Navigation panel on the left side to view the currently available features.
Add Resources
Include your assets - URDF, MJCF, Mesh, USD, Image, Video, or any kind of data.

In the Resource manager page, you can view exisitng resources or add a new one.
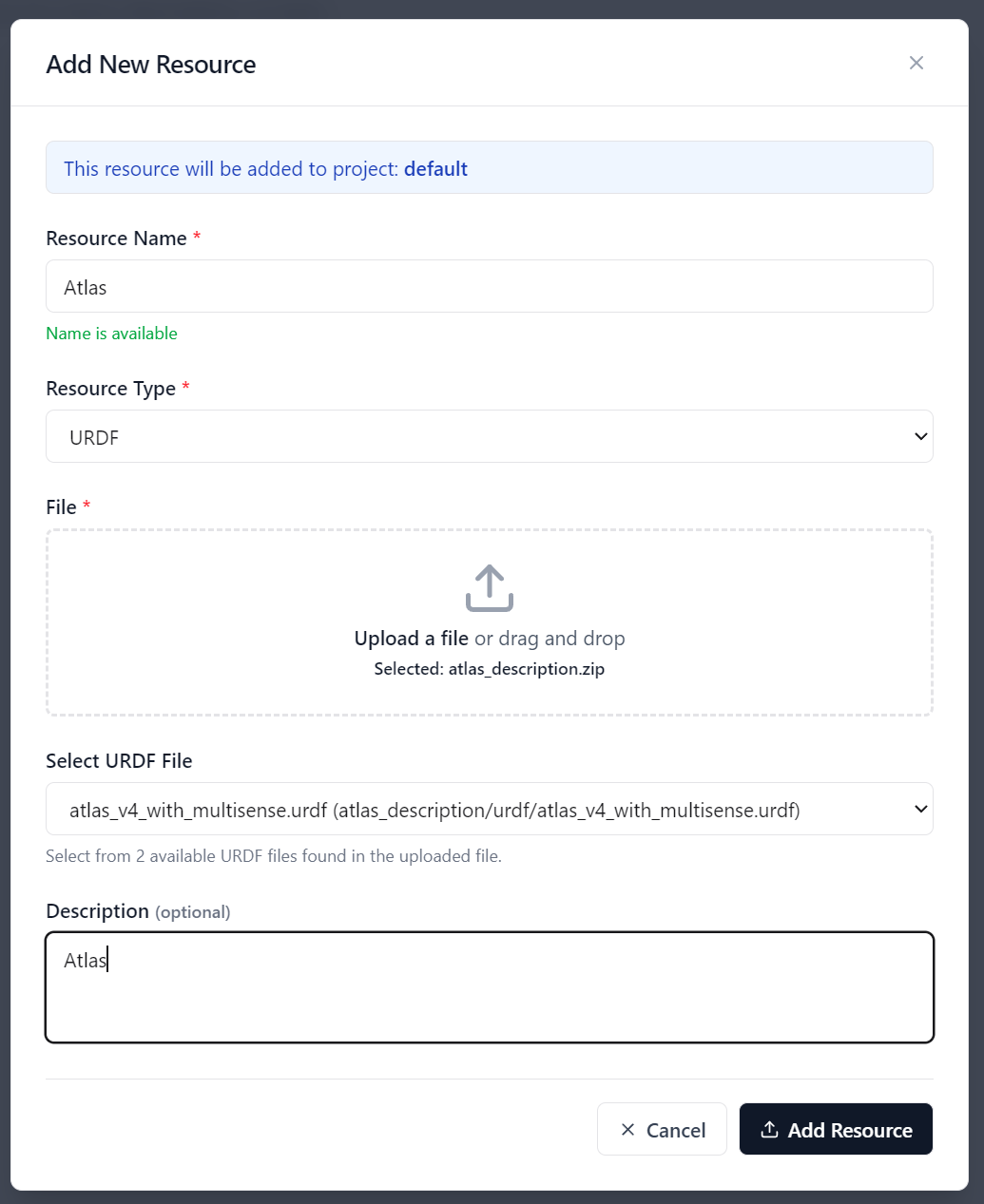
New resources can be added - if it contains multiple files, compress it to zip. The main file will be automatically detected. If there are more than one main file you can choose.
Complete Working Example
Here's a self-contained example you can run:
import humalab as hl
import random
def simulate_robot_task(speed, precision):
"""Simulate a robot task with given parameters"""
# Higher speed and precision = higher success chance
success_prob = (speed * 0.4 + precision * 0.6) / 10
success = random.random() < success_prob
# Calculate task time (inverse of speed)
time_taken = 10 / max(speed, 0.1)
return {
"success": success,
"time": time_taken,
"score": success_prob * 100
}
# Initialize and run experiment with context manager
total_success = 0
with hl.init(
project="robotics",
name="speed_precision_test",
tags=["robot", "test"],
scenario={
"robot_speed": "${uniform: 1, 10}",
"precision": "${gaussian: 5, 0.02}"
},
api_key="your_api_key"
) as run:
# Add metrics to track
success_metric = hl.metrics.Metrics()
run.add_metric("success_rate", success_metric)
# Execute experiment
for i in range(50):
with run.create_episode() as episode:
# Run simulation with sampled parameters
# result = simulate_robot_task(
# speed=episode.robot_speed,
# precision=episode.precision
# )
# Log episode results
episode.log(result)
# Update run metrics
if result["success"]:
total_success += 1
run.log({
"success_rate": total_success / (i + 1)
})
print(f"Experiment complete! Success rate: {total_success/50:.1%}")Next Steps
Now that you've run your first experiment:
- Learn more about Scenarios - Explore all available distributions
- Understand Runs & Episodes - Master the experiment lifecycle
- Track Metrics - Learn advanced metric tracking
- Browse API Reference - Detailed API documentation
Troubleshooting
Authentication Issues
If you get authentication errors:
# Make sure you've called init or login
hl.init(api_key="your_api_key")
# Or use interactive login
hl.login()Import Errors
Make sure HumaLab is installed:
pip install --upgrade humalabGetting Help
- GitHub Issues: github.com/humalab/humalab_sdk
- Email: info@humalab.ai
- Documentation: This site!
