API Reference
Complete reference for the HumaLab SDK API.
Core Functions
init()
Initialize a new HumaLab run as a context manager.
humalab.init(
project: str | None = None,
name: str | None = None,
description: str | None = None,
id: str | None = None,
tags: list[str] | None = None,
scenario: str | list | dict | Scenario | None = None,
scenario_id: str | None = None,
seed: int | None = None,
auto_create_scenario: bool = False,
base_url: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
timeout: float | None = None
) -> Generator[Run, None, None]Parameters:
project: The project name under which to create the runname: The name of the rundescription: A description of the runid: The unique identifier for the run (auto-generated if None)tags: A list of tags to associate with the runscenario: The scenario configuration as a string, list, dict, or Scenario instancescenario_id: The unique identifier of a pre-defined scenario to useseed: An optional seed for scenario randomizationauto_create_scenario: Whether to automatically create the scenario if it does not existbase_url: The base URL of the HumaLab serverapi_key: The API key for authenticationtimeout: The timeout for API requests
Example:
import humalab as hl
# Using a dict
with hl.init(
project="my_project",
name="experiment_1",
scenario={"param": "${uniform: 0, 10}"},
api_key="your_api_key"
) as run:
episode = run.create_episode()
with episode:
# Run validation
pass
# Or using a Scenario instance
from humalab.scenarios import Scenario
scenario = Scenario()
scenario.init(scenario={"param": "${uniform: 0, 10}"}, seed=42)
with hl.init(
project="my_project",
name="experiment_2",
scenario=scenario,
api_key="your_api_key"
) as run:
episode = run.create_episode()
# The scenario is already initialized with seed=42
passlogin()
Configure HumaLab authentication and connection settings.
humalab.login(
api_key: str | None = None,
relogin: bool | None = None,
host: str | None = None,
force: bool | None = None,
timeout: float | None = None
) -> boolParameters:
api_key: API key for authenticationhost: API host URLtimeout: Request timeout in secondsrelogin: (unused, for compatibility)force: (unused, for compatibility)
Returns:
bool: Always returns True
Example:
import humalab as hl
hl.login(api_key="your_api_key", host="https://api.humalab.ai")finish()
Finish the current run.
humalab.finish(
status: RunStatus = RunStatus.FINISHED,
err_msg: str | None = None
)Parameters:
status: The final status of the run (defaults to FINISHED)err_msg: Optional error message if the run errored
Example:
hl.finish() # Mark run as finisheddiscard()
Discard the current run by finishing it with CANCELED status.
humalab.discard()Example:
hl.discard() # Cancel the runScenario Class
Scenario()
Create a new scenario instance.
from humalab.scenarios import Scenario
scenario = Scenario()Scenario.init()
Initialize the scenario with configuration.
scenario.init(
scenario: str | list | dict | None = None,
seed: int | None = None,
scenario_id: str | None = None
)Parameters:
scenario: Scenario configuration (YAML string, list, or dict)seed: Random seed for reproducibilityscenario_id: Scenario identifier (format: "name:version")
Example:
scenario.init(
scenario={"param": "${uniform: 0, 10}"},
seed=42,
scenario_id="my_scenario:1"
)Scenario.resolve()
Resolve the scenario by sampling distributions.
scenario.resolve() -> tuple[DictConfig | ListConfig, dict]Returns:
- Tuple of (resolved_config, episode_values)
Example:
config, vals = scenario.resolve()Scenario Properties
scenario.template # Get scenario template (OmegaConf)
scenario.yaml # Get scenario as YAML string
scenario.scenario_id # Get scenario ID (str | None)
scenario.seed # Get random seed (int | None)Example:
from humalab.scenarios import Scenario
scenario = Scenario()
scenario.init(
scenario={"param": "${uniform: 0, 10}"},
scenario_id="my_scenario:1",
seed=42
)
print(f"Scenario ID: {scenario.scenario_id}") # Output: my_scenario
print(f"Seed: {scenario.seed}") # Output: 42
print(f"Template: {scenario.template}")
print(f"YAML: {scenario.yaml}")Scenario Operations
list_scenarios()
List all scenarios for a given project.
from humalab.scenarios import list_scenarios
scenarios = list_scenarios(
project: str = "default",
limit: int = 20,
offset: int = 0,
include_inactive: bool = False,
search: str | None = None,
status_filter: str | None = None,
base_url: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
timeout: float | None = None
) -> list[ScenarioMetadata]Parameters:
project: The project name to list scenarios from (defaults to "default")limit: Maximum number of scenarios to return (defaults to 20)offset: Number of scenarios to skip for pagination (defaults to 0)include_inactive: Whether to include inactive scenarios (defaults to False)search: Search query to filter scenarios by name or descriptionstatus_filter: Filter scenarios by statusbase_url: The base URL of the HumaLab APIapi_key: The API key for authenticationtimeout: The timeout for API requests in seconds
Returns:
list[ScenarioMetadata]: A list of scenario metadata objects
Example:
from humalab.scenarios import list_scenarios
# List all scenarios
scenarios = list_scenarios(project="my_project")
for scenario in scenarios:
print(f"{scenario.name} v{scenario.version}: {scenario.description}")get_scenario()
Retrieve and initialize a scenario from HumaLab.
from humalab.scenarios import get_scenario
scenario = get_scenario(
scenario_id: str,
version: int | None = None,
project: str = "default",
seed: int | None = None,
base_url: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
timeout: float | None = None
) -> ScenarioParameters:
scenario_id: The unique identifier of the scenarioversion: Optional specific version to retrieveproject: The project name (defaults to "default")seed: Optional seed for scenario randomizationbase_url: Optional API host overrideapi_key: Optional API key overridetimeout: Optional timeout override
Returns:
Scenario: The initialized scenario instance
Example:
from humalab.scenarios import get_scenario
# Get specific scenario
scenario = get_scenario(
scenario_id="abc123",
version=2,
project="my_project",
seed=42
)
# Use in a run
run = hl.Run(scenario=scenario, name="test_run")Run Class
Run()
Create a new run instance.
from humalab import Run
run = Run(
scenario: Scenario,
project: str = "default",
name: str | None = None,
description: str | None = None,
id: str | None = None,
tags: list[str] | None = None,
base_url: str | None = None,
api_key: str | None = None,
timeout: float | None = None
)Parameters:
scenario: Scenario instance (required)project: Project name for organizationname: Run namedescription: Run descriptionid: Custom run ID (auto-generated if not provided)tags: List of tagsbase_url: Custom API endpointapi_key: API keytimeout: Request timeout in seconds
Example:
run = Run(
scenario=scenario,
project="my_project",
name="experiment_1",
description="Testing new parameters",
tags=["experiment", "v1"]
)Run.create_episode()
Create a new episode.
run.create_episode(
episode_id: str | None = None
) -> EpisodeParameters:
episode_id: Custom episode ID (auto-generated if not provided)
Returns:
- Episode instance
Example:
episode = run.create_episode()Run.add_metric()
Add a metric to the run.
run.add_metric(
name: str,
metric: Metrics
)Parameters:
name: Metric namemetric: Metrics instance
Example:
from humalab.metrics import Metrics
metric = Metrics()
run.add_metric("score", metric)Run.log()
Log data to run metrics.
run.log(
data: dict,
x: dict | None = None,
replace: bool = False
)Parameters:
data: Dictionary of metric name -> valuex: Dictionary of metric name -> x-axis valuereplace: Replace last value instead of appending
Example:
run.log({"score": 0.95}, x={"score": 0})
run.log({"score": 0.97}, x={"score": 1})Run.log_code()
Log code content as an artifact.
run.log_code(
key: str,
code_content: str
)Parameters:
key: Artifact keycode_content: Code content string
Example:
with open("agent.py") as f:
run.log_code("agent", f.read())Run.finish()
Finish the run and upload metrics.
run.finish(
status: RunStatus = RunStatus.FINISHED,
err_msg: str | None = None
)Parameters:
status: Final run statuserr_msg: Error message (if errored)
Example:
from humalab.humalab_api_client import RunStatus
run.finish(status=RunStatus.FINISHED)Run Properties
run.id # Run ID
run.name # Run name
run.description # Run description
run.tags # Run tags
run.project # Project name
run.scenario # Scenario instanceEpisode Class
Episodes are created via run.create_episode().
Episode.log()
Log data to episode.
episode.log(data: dict)Parameters:
data: Dictionary of key-value pairs to log
Example:
episode.log({
"reward": 100.0,
"steps": 150,
"success": True
})Episode.log_code()
Log code artifact for this episode.
episode.log_code(
key: str,
code_content: str
)Parameters:
key: Artifact keycode_content: Code content
Episode.finish()
Finish the episode.
episode.finish(
status: EpisodeStatus = EpisodeStatus.FINISHED,
err_msg: str | None = None
)Parameters:
status: Episode statuserr_msg: Error message (if errored)
Example:
from humalab.humalab_api_client import EpisodeStatus
episode.finish(status=EpisodeStatus.FINISHED)Episode Properties
episode.episode_id # Episode ID
episode.run_id # Parent run ID
episode.scenario # Resolved scenario config (DictConfig | ListConfig)
episode.episode_vals # Sampled parameter values (dict)
episode.is_finished # Whether episode is finished (bool)
episode.status # Episode status (EpisodeStatus)Accessing Scenario Configuration
Episodes provide convenient ways to access scenario configuration values:
# Access via property
config = episode.scenario
print(config.param1)
# Access via attribute (recommended)
value = episode.param1
# Access via subscript
value = episode["param1"]
# Nested access
robot_speed = episode.robot.speedExample:
scenario.init(scenario={
"robot": {
"speed": "${uniform: 1, 10}",
"precision": "${gaussian: 0.5, 0.1}"
}
})
episode = run.create_episode()
# All these work:
speed1 = episode.scenario.robot.speed
speed2 = episode.robot.speed
speed3 = episode["robot"]["speed"]Metrics Class
Metrics()
Create a metrics instance.
from humalab.metrics import Metrics
from humalab.constants import GraphType
metric = Metrics(
graph_type: GraphType = GraphType.LINE
)Parameters:
graph_type: Graph visualization type (defaults to LINE). The metric dimensionality is automatically determined from the graph type.
Example:
metric = Metrics(
graph_type=GraphType.LINE
)Metrics.log()
Log a data point.
metric.log(
data: Any,
x: Any = None,
replace: bool = False
)Parameters:
data: Data valuex: X-axis value (optional)replace: Replace last value
Metrics.finalize()
Finalize metric data (called automatically).
metric.finalize() -> dictSummary Class
Summary metrics aggregate logged values into a single statistic.
Summary()
Create a summary metric instance.
from humalab.metrics import Summary
summary = Summary(
summary: str = "last"
)Parameters:
summary: The aggregation method. Supported values:"min": Minimum value"max": Maximum value"mean": Mean/average value"first": First logged value"last": Last logged value (default)"none": No aggregation
Example:
from humalab.metrics import Summary
# Create summary metrics
max_score = Summary(summary="max")
avg_reward = Summary(summary="mean")
run.add_metric("best_score", max_score)
run.add_metric("avg_reward", avg_reward)
# Log values
run.log({"best_score": 95.0, "avg_reward": 87.5})
run.log({"best_score": 98.0, "avg_reward": 89.2})
# Final: best_score=98.0, avg_reward=88.35ScenarioStats Class
Automatically tracks scenario parameter distributions and episode outcomes.
ScenarioStats()
ScenarioStats metrics are created automatically when you use distributions in scenarios. They track:
- Sampled values for each parameter
- Episode status for each sample
- Distribution type and configuration
Example:
# Scenario stats are created automatically
scenario.init(scenario={
"learning_rate": "${log_uniform: 0.001, 0.1}",
"batch_size": "${categorical: [32, 64, 128], [0.3, 0.5, 0.2]}"
})
# ScenarioStats for both parameters are automatically tracked
# - learning_rate: log_uniform distribution stats
# - batch_size: discrete distribution statsScenarioStats.log_status()
Log the status of an episode (called automatically).
scenario_stat.log_status(
episode_id: str,
episode_status: EpisodeStatus,
replace: bool = False
)Parameters:
episode_id: The unique identifier of the episodeepisode_status: The status of the episodereplace: Whether to replace an existing status
Raises:
ValueError: If status for the episode_id already exists and replace is False
Constants
MetricDimType
from humalab.constants import MetricDimType
MetricDimType.ONE_D # One-dimensional
MetricDimType.TWO_D # Two-dimensional
MetricDimType.THREE_D # Three-dimensionalGraphType
from humalab.constants import GraphType
GraphType.LINE # Line graph
GraphType.HISTOGRAM # Histogram
GraphType.BAR # Bar chart
GraphType.SCATTER # Scatter plot
GraphType.GAUSSIAN # Gaussian distribution
GraphType.THREE_D_MAP # 3D visualizationEpisodeStatus
from humalab.humalab_api_client import EpisodeStatus
EpisodeStatus.FINISHED # Successfully completed
EpisodeStatus.ERRORED # Encountered error
EpisodeStatus.CANCELED # Canceled
EpisodeStatus.TIMEOUT # Timed outRunStatus
from humalab.humalab_api_client import RunStatus
RunStatus.FINISHED # Successfully completed
RunStatus.ERRORED # Encountered error
RunStatus.CANCELED # CanceledAssets Module
HumaLab provides asset management capabilities:
from humalab import assets
# Archive operations
# Resource file management
# URDF file handlingDistribution Functions
Available in scenario configurations:
Scalar (0D) Distributions
"${uniform: min, max}"
"${gaussian: mean, std}"
"${truncated_gaussian: mean, std, min, max}"
"${log_uniform: min, max}"
"${bernoulli: p}"
"${categorical: values, probs}"
"${discrete: low, high, endpoint}"Multi-Dimensional Distributions
Important: 1D uses same scalar parameters as 0D. 2D and 3D use array parameters.
# 1D (same parameters as 0D, returns 1-element array)
"${uniform_1d: min, max}"
"${gaussian_1d: mean, std}"
"${truncated_gaussian_1d: mean, std, min, max}"
"${log_uniform_1d: min, max}"
"${bernoulli_1d: p}"
"${categorical_1d: values, probs}"
"${discrete_1d: low, high, endpoint}"
# 2D (array parameters)
"${uniform_2d: [min, min], [max, max]}"
"${gaussian_2d: [mean, mean], [std, std]}"
"${truncated_gaussian_2d: [mean, mean], [std, std], [min, min], [max, max]}"
# 3D (array parameters)
"${uniform_3d: [min, min, min], [max, max, max]}"
"${gaussian_3d: [mean, mean, mean], [std, std, std]}"
"${truncated_gaussian_3d: [mean, mean, mean], [std, std, std], [min, min, min], [max, max, max]}"Error Handling
Common Exceptions
# ValueError: Invalid parameters or reserved names
try:
run.log({"scenario": value}) # "scenario" is reserved
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
try:
run.log({"seed": value}) # "seed" is reserved
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# ValueError: Metric already exists
try:
run.log({"metric": value})
run.log({"metric": value}) # Without replace=True
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")Reserved Names
The following names are reserved and cannot be used for metrics or artifacts:
scenario- Reserved for the scenario YAML configurationseed- Reserved for the scenario random seed
Context Manager Support
Both Run and Episode support context managers:
# Automatic cleanup with context managers
with run:
episode = run.create_episode()
with episode:
# Your code here
pass
# Episode automatically finishes
# Run automatically finishesUse GUI
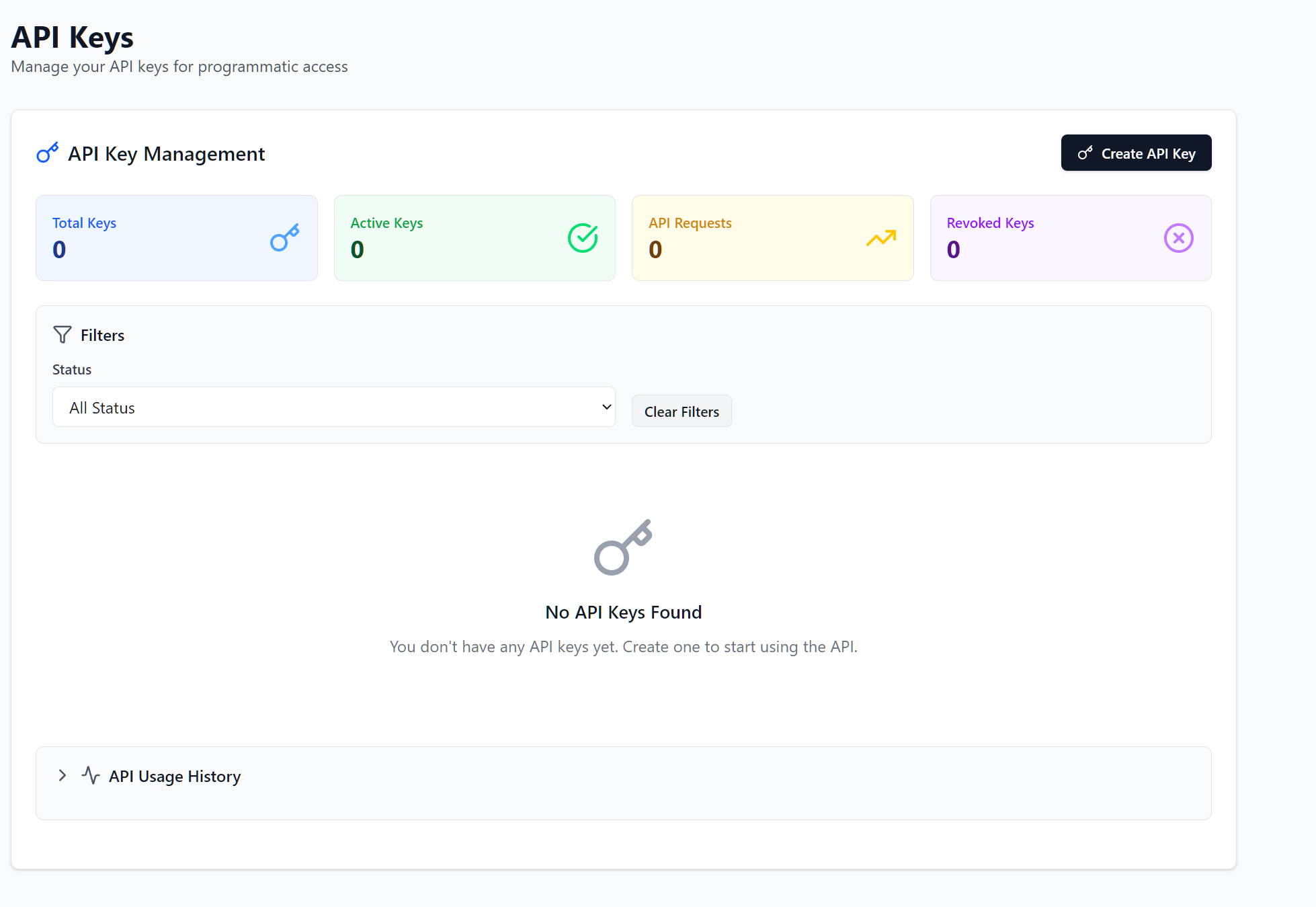
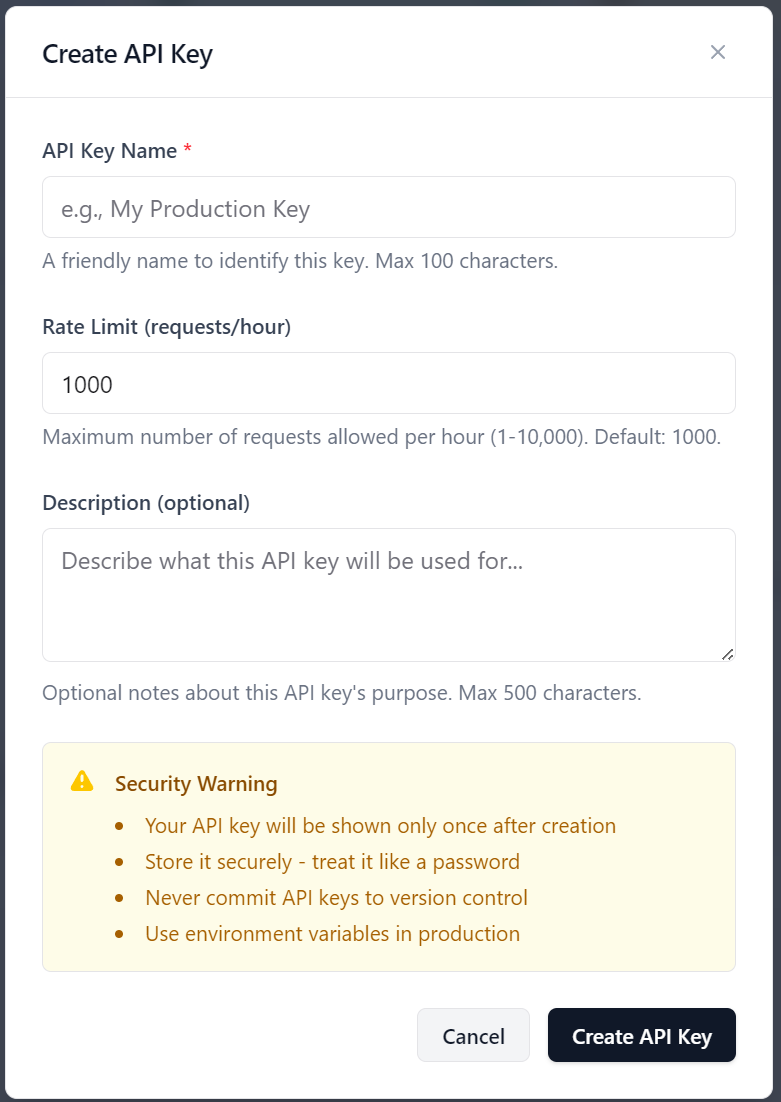
You can view the API Key status and history of each of the keys. You can also create new API keys here.